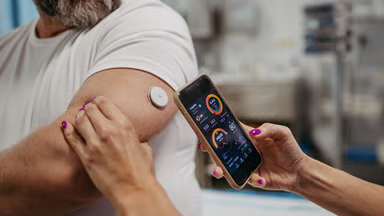
Managing Type 2 diabetes goes far beyond medication and blood glucose monitoring — what and how you eat plays a central role in stabilizing blood sugar, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing.
While traditional dietary guidance focuses on general rules, advances in artificial intelligence (AI) now make it possible to tailor nutrition to each person’s metabolic responses — offering a precision approach to diet that can improve outcomes and daily lifestyle management.
This guide explains the science of healthy diets for Type 2 diabetes and how AI-powered personalized nutrition can take it further.





Why Diet Matters in Type 2 Diabetes
According to the CDC, more than 37 million Americans have diabetes, with type 2 accounting for the majority of cases.Type 2 diabetes is characterized by high blood glucose levels and insulin resistance.
According to a Research From American Diabetes Association (ADA), nutrition therapy is a cornerstone of managing type 2 diabetes and improving glycemic control.
It shows that nutrition therapy itself can significantly improve glycemic control, sometimes as much as medication changes.
A diabetes-focused eating plan helps by:
- Controlling post-meal blood glucose spikes through choosing appropriate carbohydrates.
- Supporting weight management, which improves insulin sensitivity.
- Reducing cardiovascular risks by emphasizing heart-healthy foods.
In fact, structured nutrition plans delivered by dietitians have shown meaningful reductions in HbA₁c — a key marker of long-term glucose control — up to 1–2% in some studies.





Core Principles of a Healthy Diet for Type 2 Diabetes
1. Balanced Dietary Patterns
Scientific reviews highlight several dietary patterns that help manage blood glucose:
- Mediterranean Diet (rich in vegetables, legumes, whole grains, olive oil)
- Low-carbohydrate diets
- Plant-based and low-glycemic index diets — all linked with improved glucose control and cardiometabolic health.
These patterns focus on whole foods, balanced macronutrient distribution, and reduced refined carbohydrates — unlike ultra-processed diets linked with higher diabetes risk.





2. Portion Control & Regular Meal Timing
Keeping carbohydrate intake consistent across meals and spacing them evenly helps the body manage blood glucose. Eating three regular meals per day and not going more than ~6 hours without a meal supports stable glycemic patterns.





3. Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods
A healthy diabetes diet focuses on:
- Non-starchy vegetables (spinach, broccoli)
- Whole grains (quinoa, oats)
- Lean protein sources (fish, legumes)
- Healthy fats (nuts, olive oil)
- Fiber-rich foods that slow glucose absorption
These choices help with satiety and support metabolic control.





4. Limit Added Sugars and Ultra-Processed Foods
Reducing sugary drinks, sweets, and highly processed foods helps prevent sharp rises in blood glucose and supports long-term metabolic health.





From Generic Plans to AI-Personalized Nutrition
Traditional dietary recommendations are broad and often one-size-fits-all, but research shows that individuals can respond very differently to the same foods. Unique metabolic and lifestyle factors mean that two people eating the same meal may experience very different blood glucose curves.
That’s where AI-driven personalized nutrition comes in.
What AI Personalized Nutrition Does
AI systems analyse multiple data streams, including:
- Medical history and lab values
- Lifestyle patterns and activity
- Dietary preferences and restrictions
- Data from wearables and glucose sensors
This allows AI to tailor food choices and meal timing based on how each person’s body responds — not just on broad guidelines.
Emerging research into personalized nutrition demonstrates potential benefits for improving glucose outcomes (like HbA₁c and postprandial glucose responses) and adapting plans as a person’s metabolic profile changes.





Benefits of AI-Powered Personalized Nutrition
Dynamic, Real-Time Adjustments
AI algorithms can refine meal recommendations as new data comes in — a crucial advantage over static meal plans.
Greater Relevance & Adherence
Personalization increases relevance, making it easier for individuals to stick with their diet long term.
Actionable Feedback
Instead of generic advice (“reduce carbs”), AI platforms offer specific swaps and portions — e.g., choosing quinoa over white rice to manage glucose response.
Insights for Clinicians
Automated reports support clinicians by identifying patterns and areas needing intervention, saving time and improving care decisions.





Integrating Nutrition into Everyday Life
A healthy diet for Type 2 diabetes isn’t just about short-term glucose control — it’s about long-term lifestyle change.
Small consistent changes matter:
Adding fiber, choosing healthier fats, balancing carbs, and eating at regular times all contribute to better blood sugar stability.
Incremental progress is sustainable:
Gradual adjustments are more practical and easier to maintain compared to drastic diet changes.





Conclusion
A healthy diet for Type 2 diabetes combines evidence-based nutrition principles with individualized strategies that address real metabolic responses.
Advances in AI-powered personalized nutrition take this a step further by tailoring meal plans and food recommendations to each person’s unique physiology and lifestyle. This approach has the potential to enhance glycemic control, support sustainable behavior change, and empower patients and clinicians to work together more effectively.
Take Control of Your Healthy Diet for Type 2 Diabetes — With Real-Time Support
Understanding what to eat is the first step.
Tracking how your body responds is what creates real progress.
If you want to move beyond generic meal plans and start making data-driven decisions about your diet, tools that monitor food intake, glucose trends, and activity levels can make a meaningful difference in day-to-day management.
Friska CCM is designed to support individuals managing Type 2 diabetes by collecting real-time updates — from meals and exercise to glucose patterns — helping you stay informed and consistent with your nutrition goals.
Instead of guessing how certain foods affect your blood sugar, you can track, review, and adjust based on real insights.